
What is hyaluronic acid and why is it in so many skincare products?
Hyaluronic acid (HA): this ingredient commonly found in moisturizers, serums and sheet masks is an important addition to your daily skincare routine.
Why? Well, that’s because HA is a molecule that occurs naturally in the skin, helping to bind water to collagen and trapping it in the skin so that it appears plumper and more hydrated.
What even is hyaluronic acid?
Hyaluronic acid, or hyaluronan, is a natural component found in various areas of the human body, including the skin, eyes, and synovial fluid of the joints. However, for use in cosmetic products, HA is chemically derived from mucopolysaccharides (also known as glycosaminoglycans, which are negatively-charged polysaccharide compounds composed of repeating disaccharide units). Also, HA can be derived through a bacterial fermentation process, using plant materials as nutrients for the bacteria.
The physicochemical properties of HA are responsible for its vital biological abilities such as moisture retention, and physiological functions, such as skin hydration ability, lubrication, and diminishing aging symptoms.
Why is hyaluronic acid so important?
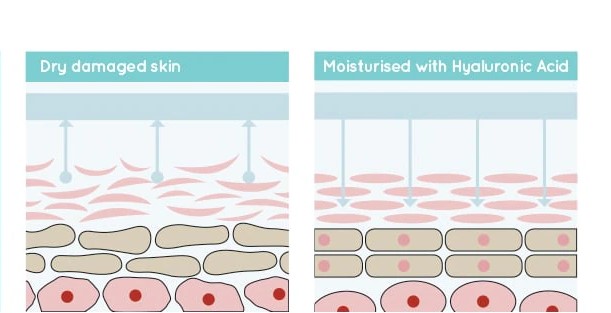
As we age, we naturally lose collagen and hyaluronic acid, so the skin easily becomes dehydrated. On top of that, an unfavorable climate, heaters during wintertime, certain skincare products and underlying skin conditions can cause tiny breaks in the protective skin barrier, causing water loss. That’s why creating a skincare routine with moisturizing products can be helpful.
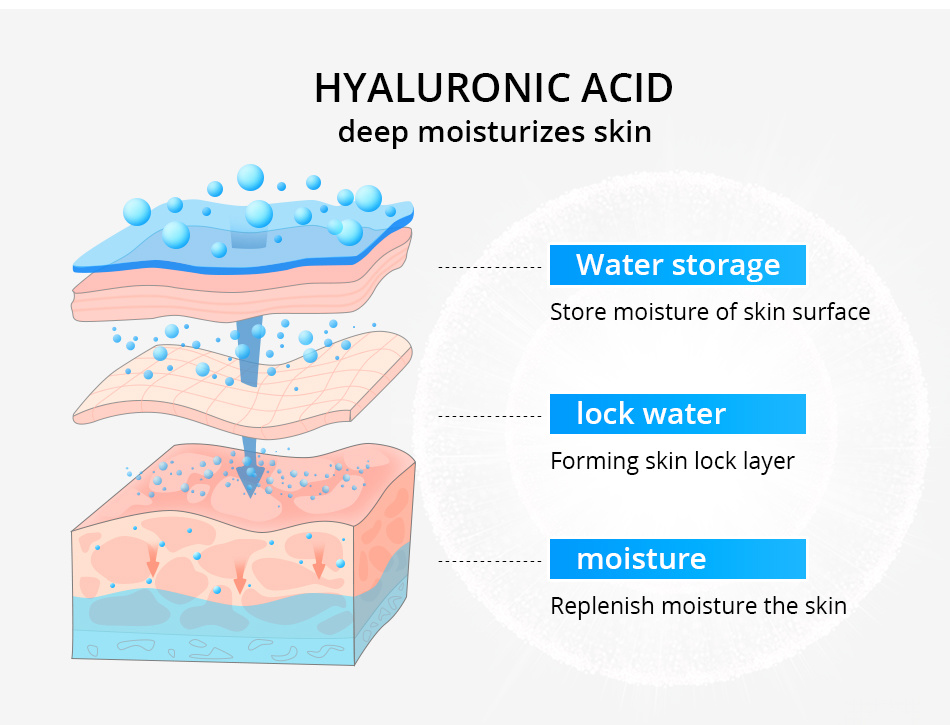
Hyaluronic acid has several benefits such as easy penetration, lightweightness, and an ability to lock in moisture from the environment and deeper dermis to hydrate the skin.
Since dehydrated skin is one of the main causes of wrinkles, hyaluronic acid also replenishes lost moisture and helps reduce the appearance of any fine lines.
Use of hyaluronic acid in cosmetology
Nowadays, HA is one of the most widely used active ingredients in cosmetic formulations. It’s evident that the skin is an indicator of an individual’s health and HA is one of the main contributors to healthy skin.
Why? Because of its hydrophilic nature, HA can be used as a moisturizing component in skincare formulations.
In cosmetic formulations, hyaluronic acid also has the function of a viscosity modifier and/or a skin conditioning agent (that has emollient, occlusive and humectant properties). That said, HA is mainly used in anti-aging cosmetic products.
Additionally, the HA average molecular weight can influence its physico-chemical properties such as biological activity and penetration into the skin.
For example, HA with LMW (low molecular weight) has the ability to enhance the level of moisture of the skin and accelerate regeneration. While HA with HMW (high molecular weight) has an occlusive effect (the ability of a substance to form a physical barrier on top of the skin), which prevents moisture loss and helps to keep skin hydrated and protected from environmental stressors.
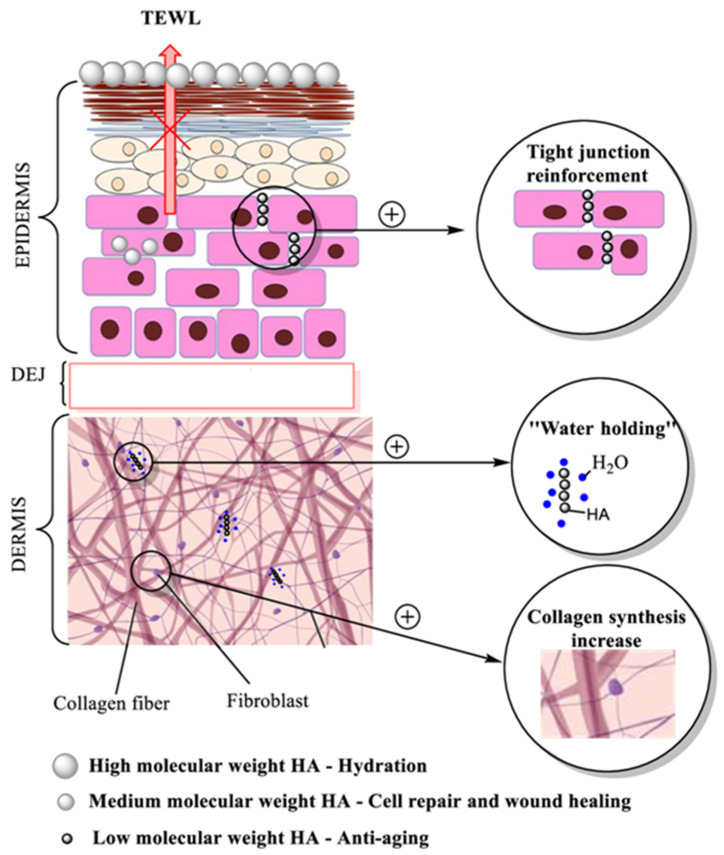
HA is also particularly important for delivery of active ingredients. It has been proven that HA enhances the penetration of the active ingredient through the stratum corneum (SC), which behaves as a barrier to the entry of the molecule into the deeper layers of the skin. HA is dually responsible for holding and locating the active ingredient in the epidermis.
Hydration effect of hyaluronic acid in cosmetic formulations
HA has the ability to bind water up to 1000 times its volume. As a result, it contributes to cellular growth, adhesion, and membrane receptor function.
The major biologic role of HA in the intercellular matrix is to reinforce the intracellular structures and produce the elastoviscous fluid matrix that firmly envelops collagen and elastin fibers.
HA holds moisture, as well as provides firmness and radiance to the skin. It can be used topically to regenerate the skin and support hydration. Even so, its very high molecular weight prevents its penetration through the SC.
Anti-aging effect of HA in cosmetic formulations
HA has an important role when it comes to skin aging.
Although HA is naturally and constantly renewed, its renewal tends to slow with age. Cells lose their ability to produce HA and skin becomes drier, thinner, and looser, leading to wrinkling, among other significant changes. It’s also associated with declining skin moisture.
In other words, it’s best to act very early, sustaining an optimal hyaluronic acid turnover similar to that of young skin, to prevent the signs of aging.
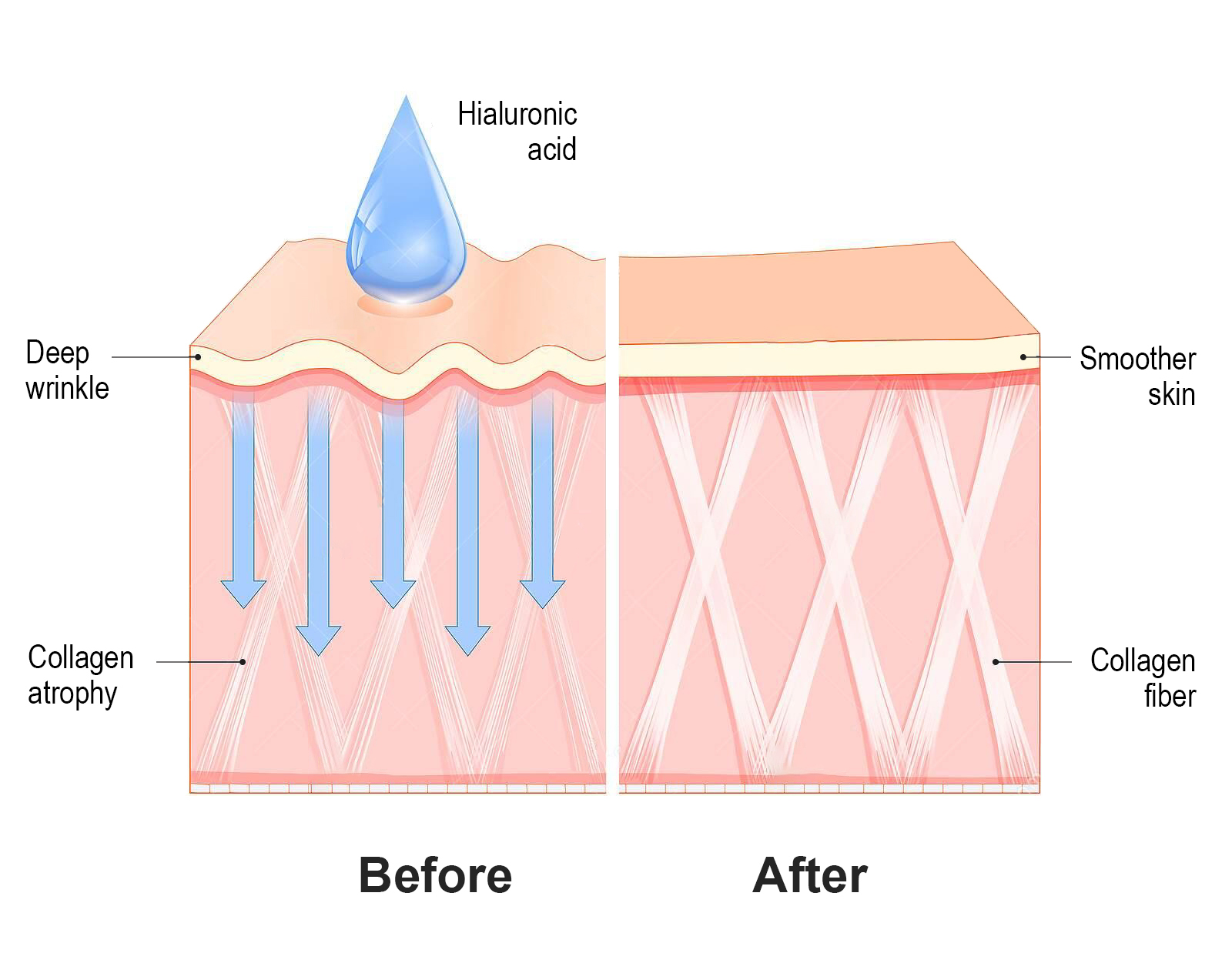
In relation to its biological effects at skin level, hyaluronic acid is actively involved in skin cell signaling and thus influences the ECM (extracellular matrix) stability. HA has an impact on the growth of keratinocytes, which protect the epidermis from aging, and it has an elasticity effect in cosmetic preparations.
Additionally, the chemical double-binding structure means HA has antioxidant properties.. It also prevents the proliferation of the skin cells and has anti-inflammatory properties on the skin.
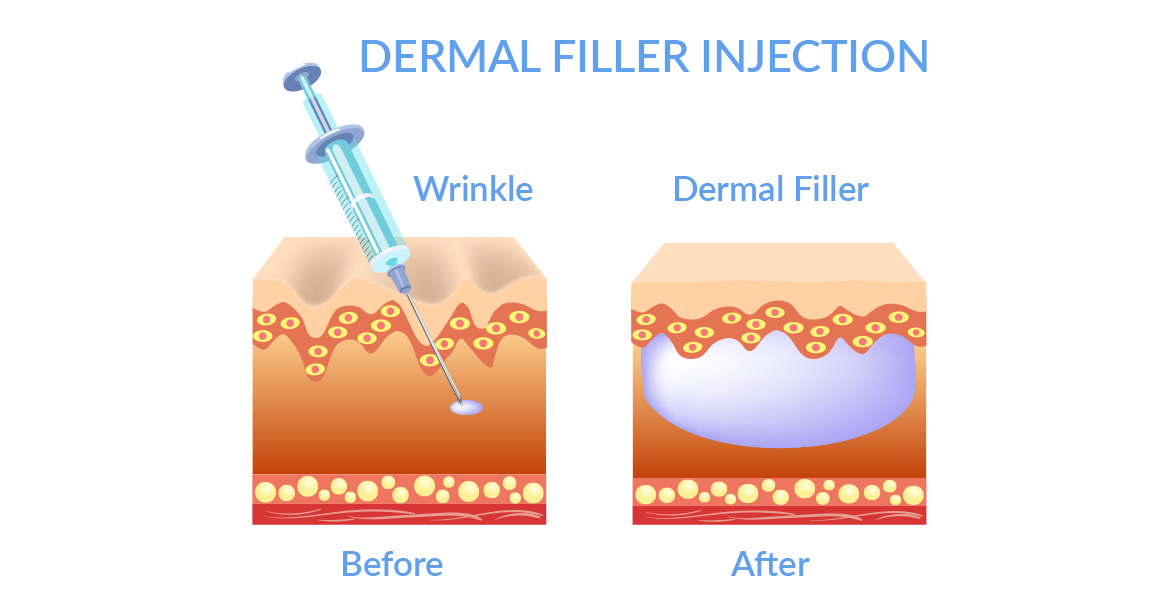
A note on HA injectables
As well as in topical skincare products, hyaluronic acid also comes in the form of an injection and a gel-like product in dermal fillers.
This cross-linked HA has become a desirable aesthetic procedure. Many are looking to rejuvenate the skin and compensate for the age-related loss and, overall, diminish age-related symptoms.
Once injected, HA attracts water to regenerate volume and recreate lost structure. Dermal fillers, in particular, can help reduce the sunken or sagging appearance of the face and soften the overall look of lines and wrinkles.
This procedure is not invasive but needs to be performed by an expert specialist. Another benefit of dermal fillers is that they’re reversible and can be dissolved by inserting an enzyme hyaluronidase.
Although injecting HA into the dermis would minimize the hallmarks of aging and boost skin volume and elasticity, don’t forget about your usual skincare routine.
Who should use hyaluronic acid?
Hyaluronic acid is suitable for all skin types. It’s non-irritating and doesn’t trigger acne, rosacea, or allergic skin reactions.
There is, however, a small chance of adverse side effects. Therefore, we recommend that you talk to your doctor if you do experience side effects from a product that contains it. This could be due to another active or inactive ingredient.
Skin types that definitely benefit the most from using hyaluronic acid are those with dry and/or more mature skin. As we already know, our bodies produce less hyaluronic acid with aging, so replacing it topically will make the most impact on those skin types.
HA also has calming and anti-inflammatory properties on sensitive skin. However, if you want to avoid the potential drying effects of high-percentage hyaluronic acid solutions,make sure that the products you’re using contain hydrolyzed hyaluronic acid, which tends to be the best ingredient for sensitive skin.
Final thoughts
Knowing all that, I encourage you to try either our daily protecting moisturizing cream based on hyaluronic acid that hydrates your skin and makes it more firm and supple. Our complementary skin-reviving night cream also features hyaluronic acid and rejuvenates your skin while you sleep.
LITERATURE:
- Juncan AM, Moisă DG, Santini A, Morgovan C, Rus LL, Vonica-Țincu AL, Loghin F. Advantages of Hyaluronic Acid and Its Combination with Other Bioactive Ingredients in Cosmeceuticals. Molecules. 2021 Jul 22;26(15):4429. doi:10.3390/molecules26154429.
- Al-Halaseh LK, Al-Jawabri NA, Tarawneh SK, Al-Qdah WK, Abu-Hajleh MN, Al-Samydai AM, Ahmed MA. A review of the cosmetic use and potentially therapeutic importance of hyaluronic acid. J Appl Pharm Sci, 2022; 12(07):034–041.
- BYRDIE. (12.11.2023). https://www.byrdie.com/what-is-hyaluronic-acid . Dostop: 29.3.2024.
- Allure. (21.3.2023). https://www.allure.com/story/what-is-hyaluronic-acid-skin-care . Dostop: 29.3.2024.
- MasterClass. (22.7.2021). https://www.masterclass.com/articles/what-is-hyaluronic-acid . Dostop: 29.3.2024.
- Harvard Health Publishing. (23.1.2022). https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/the-hype-on-hyaluronic-acid-2020012318653 . Dostop: 29.3.2024.
- Fallacara A, Baldini E, Manfredini S, Vertuani S. Hyaluronic Acid in the Third Millennium. Polymers (Basel). 2018 Jun 25;10(7):701. doi: 10.3390/polym10070701.
- DK_GLOWY (n. d.) . https://www.dkglowy.com/product/skin-reviving-night-cream-2/ . Dostop: 29.3.2024
- DK_GLOWY (n. d .) . https://www.dkglowy.com/product/skin- protecting-moisturizing-cream-2/ . Dostop: 29.3.2024